NORTHAMPTON, MA / ACCESS Newswire / September 12, 2025 / By Jocelyn Matyas, Alex Wilkins
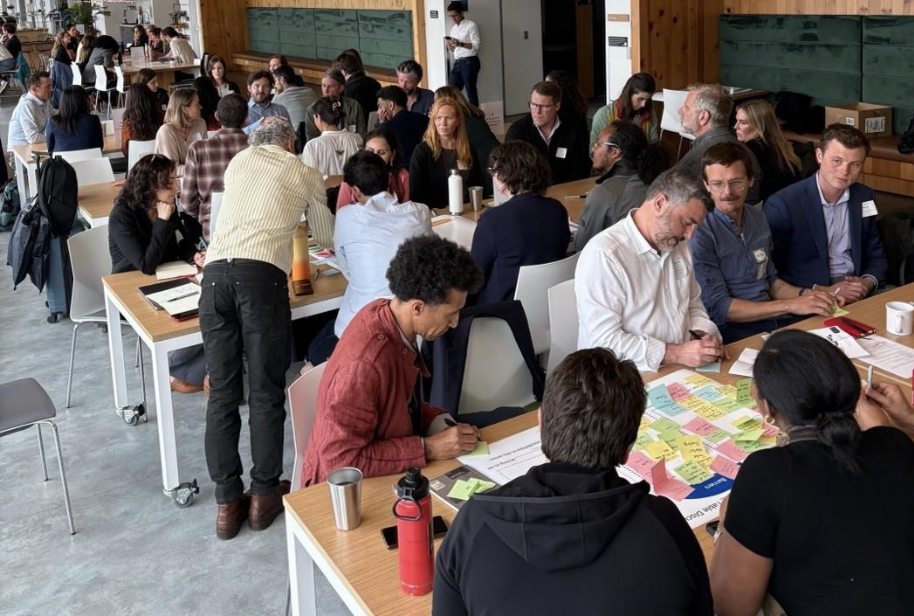

Cisco's Chief Sustainability Office hosted an AI + Climate Innovation Lab, bringing together 100+ industry experts, founders, and investors to discuss AI and data needs across nine climate sub sectors during San Francisco Climate Week 2025.
Artificial intelligence (AI) holds great promise for climate innovation, but its effectiveness depends on access to diverse, high-quality data - something that can be difficult and costly to obtain in the climate sector. This data challenge further complicates an already complex financial environment for climate tech, which is supported by a blend of public, philanthropic, and private funding.
Specifically, Cisco Foundation's grants and investments, via the Regenerative Future Fund (RFF), support quality, open source, foundational data availability and innovative AI applications for climate through blended finance for the industry. Our latest blended finance engagements -with partners across regenerative agriculture and wildfire resilience - serve as case studies.
Aligningcapital and data to value regenerative agriculture practices
U.S. farmers seeking to adopt regenerative agriculture practices face many challenges, such as limited access to capital and inadequate data infrastructure. In fact, the USDA has reported 21% and 17% declines in farm working capital in 2023 and 2024 respectively. These economic trends can limit farmers' ability to invest in regenerative transitions, and challenge long-term sustainability and growth.
To address this, we provided investment capital to the Fractal Farmer Agriculture Regenerative Management (FARM) Fund, which introduced a pioneering financial model that supports farmers while maintaining their land control. Offering 10-year contracts inclusive of incentives tied to regenerative practice adoption, Fractal provides an alternative to conventional debt or majority equity funding structures.
The success of this model is reflected in Fractal's work with 14 farms, which the organization says have reported a 6.5% higher crop yield compared to local benchmarks and maintained stronger income rates relative to market averages.
For Jesse Hough, the general manager and financial strategist of Hough Farms in East Central Nebraska, Fractal's long term minority investment approach has helped him consistently outperform county yields. He can continue making on-farm decisions and, unlike short-term programs, Fractal supports regenerative practices for the full ten years, aligning incentives so both farmer and investor share in the long-term gains.
Fractal uses AI and machine learning to analyze underlying land productivity and create more accurate land valuations for its investments. Its models incorporate climate risk and soil health, a more sophisticated approach than traditional static measures that can under- or overvalue a farm's long-term potential. For Fractal to continue to implement its work best and support farmers like Jesse, it needs improved data infrastructure to support underwriting and incentive processes for the company.
"When regenerative practices improve yield resilience, the cash flow impacts ripple from land value to crop insurance. Through Open Ground, we're partnering with Earth Genome to make the climate and agronomic data behind those benefits open source - ensuring it can drive meaningful impact across the entire sector." - Dr. Emma Fuller, Co-Founder, Fractal
To accelerate the development of these vital datasets, the Cisco Foundation also provided an early-stage cash grant to Earth Genome. Their new, open-source Open Ground initiative, developed in collaboration with Fractal, will integrate historical climate data, localized extreme weather models, and advanced crop failure classifications to deliver precise field-level insights. Their open access helps stakeholders like researchers, startups, insurers, lenders, and public good entities unlock the potential for AI applications in agriculture. It also helps them to confidently invest in, integrate and reward regenerative agricultural practices in their operations.
The AI edge in wildfire management: Mapping a resilient future
Another example of our blended finance approach is our support of Vibrant Planet and Vibrant Planet Data Commons to address wildfire and land management.
Cisco Foundation's investee, Vibrant Planet PBC, operates on the core thesis that "you can't understand what you can't see" - a concept increasingly crucial as more extreme weather, outdated fire suppression policies, and fragmented restoration efforts make U.S. forests more susceptible to catastrophic wildfires.
The lack of open-source, high-quality data has hindered restoration, management, and community engagement, and has especially excluded Indigenous stewardship and perspectives.
Addressing these challenges requires advanced technology. Vibrant Planet leverages satellite imagery, remote sensing, AI-powered modeling, and cloud-based data integration to capture a comprehensive, real-time picture of forest health, fire risk, and ecosystem change with unmatched granularity.
While these technologies enable the collection, analysis, and sharing of vast datasets -spanning millions of acres - they provide it at an incredibly localized level. This makes actionable insights and informed recommendations via their wildfire resilience platform available to land managers, scientists, and policymakers.
Vibrant Planet Data Commons, the nonprofit arm of Vibrant Planet PBC, makes forest science and data meaningful and accessible to drive wildfire and ecosystem resilience. With Cisco Foundation grant support since 2022, they've built core infrastructure and released novel open-access data packages - including a wildfire ignition probability model -alongside story-driven tools for public engagement.
Their work prioritizes Indigenous knowledge sharing, with protocols co-developed alongside Tribal partners. These packages are used by scientists and practitioners across the American West, with a growing focus on tracking how this knowledge informs management and infrastructure decisions.
As Dr. Chelsey Walden-Schreiner, Director of Science Development at Vibrant Planet Data Commons shared, "Together, Vibrant Planet PBC and VPDC form a hybrid engine for change - where science meets scalable systems, and where public good and market-driven innovation reinforce one another. Our success is not parallel, but interdependent - unlocking a model for how mission-aligned for-profits and nonprofits can co-create transformative climate resilience."
Together, these examples illustrate how blended finance and open data can help inform AI-driven approaches to climate resilience, such as supporting more adaptive agricultural practices and informing forest management strategies.
This blog was written with assistance from Ryan Jones, Cisco Chief Sustainability Office, TekSystems.
View original content here.
View additional multimedia and more ESG storytelling from Cisco Systems Inc. on 3blmedia.com.
Contact Info:
Spokesperson: Cisco Systems Inc.
Website: https://www.3blmedia.com/profiles/cisco-systems-inc
Email: info@3blmedia.com
SOURCE: Cisco Systems Inc.
View the original press release on ACCESS Newswire:
https://www.accessnewswire.com/newsroom/en/industrial-and-manufacturing/cisco-the-data-catalyst-blended-finance-paving-the-way-for-climate-ai-1072220