Crunchfish AB (publ) today announces an expanded strategic positioning of its patented Governed Offline Payments architecture, highlighting how offline payment resilience can be implemented while preserving regulatory control and potentially improving funding efficiency within regulated financial institutions through a reservation-based architecture.
Digital payments are regarded as critical infrastructure. Most digital payment systems, however, depend on online connectivity and central system availability. Offline payment capability is therefore increasingly under consideration by central banks, system operators, banks, and other regulated institutions seeking to enhance resilience. Crunchfish's Governed Offline Payments architecture enables transactions to be executed offline under system-defined limits, while verification and settlement remain within the underlying payment system. Funds are not transferred to devices and no parallel store of value is created. Ledger authority, liquidity management, and regulatory oversight remain within the underlying payment system.
A distinguishing feature of Crunchfish's architecture is its reservation-based model. Offline spending capacity is defined through centrally governed reservations derived from available balances and approved credit capacity. These reservations remain on accounts held within regulated financial institutions. From a financial perspective, such reservations remain as operational balances on the balance sheets of the institutions holding the accounts and may function as stable operational balances. In banking terminology, these balances may contribute to what is commonly referred to as "float", i.e. funds that remain within the institution and may support funding efficiency, depending on product design, user terms, and applicable regulatory treatment. Unlike immediate offline models, liquidity is not removed from bank balance sheets by money transfers to devices. Unlike traditional deferred offline implementations, which typically leave institutional funding profiles unchanged, the governed offline model with reservations may contribute to structurally stable operational balances under system governance.
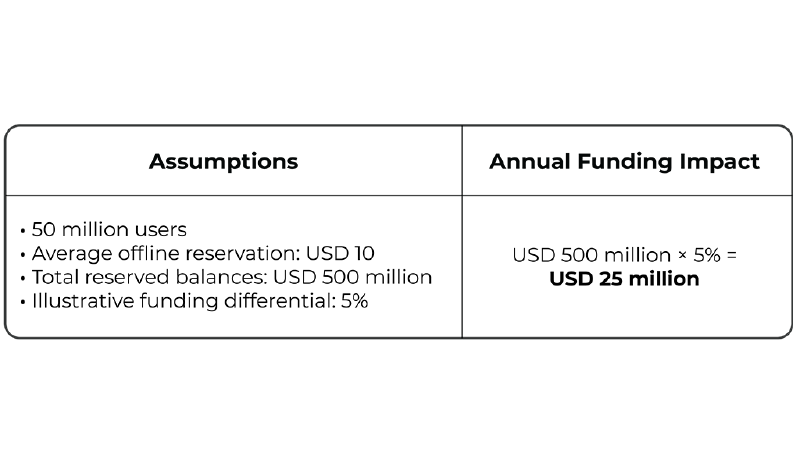
The reservation-based structure may contribute to improved funding efficiency within banks and other regulated institutions. By way of illustration only, if 50 million users maintain an average offline reservation of USD 10, this corresponds to USD 500 million in balances remaining within regulated institutions. At an assumed alternative funding cost of 5 percent, such balances could correspond to up to USD 25 million per year in avoided alternative funding cost, illustrating how reservation-backed float may influence institutional funding profiles, subject to applicable regulatory treatment. This illustrates how offline capability, when structured under governed reservations, may influence institutional funding profiles in addition to improving payment resilience.
"Offline payments are often viewed solely as a resilience measure," says Joachim Samuelsson, CEO of Crunchfish. "Our governed offline model demonstrates that resilience can be implemented without compromising settlement discipline, while supporting funding efficiency within regulated institutions. We believe this alignment strengthens the institutional relevance of offline payments and provides a stronger economic rationale for system adoption."
Crunchfish believes this strategic positioning is particularly relevant for central banks, system operators, banks, and other regulated institutions evaluating offline payment capability as part of long-term resilience, regulatory, and funding strategy considerations. The company's patented Layer-2 architecture is designed to enable system-wide deployment without modification of underlying settlement systems, and its licensing model supports both open payment systems and closed-loop wallet environments.
The company views this positioning as a strategic expansion of the value proposition of its patented technology. A detailed architectural comparison of offline payment models, including liquidity and funding implications, is available on Crunchfish's website under What We Solve. The institutional economic framework, illustrative funding example, and licensing structure are further described under Resources/Business Model.
For more information, please contact:
Joachim Samuelsson, CEO of Crunchfish AB
+46 708 46 47 88
joachim.samuelsson@crunchfish.com
This information was provided by the above for publication on February 17th, 2026, at 8:30 CET.
Västra Hamnen Corporate Finance AB is the Certified Adviser. Email: ca@vhcorp.se. Telephone +46 40 200 250.
About Crunchfish - crunchfish.com
Crunchfish is a deep fintech company developing governed offline payments technology for payment systems, banks, and payment applications. The company enables offline payments as a Layer-2 solution on top of existing payment systems, allowing transactions to be executed without connectivity while ledger authority and settlement remain unchanged. Through a reservation-based model, resilience is achieved without creating parallel forms of money or unmanaged credit risk. Crunchfish's architecture is patented and enables interoperability across multiple payment systems and markets. The solution strengthens system stability while also supporting economic incentives by ensuring that liquidity backing offline payments remains within the regulated financial system.